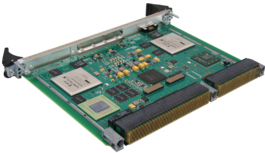
Conduction cooling is defined as the transfer of heat through solids. A common example of this is the conduction cooled chassis mounted onto a cold plate as shown in the below figure. Heat generated inside the chassis by the electronics flows into the chassis aluminum sidewalls and down into the cold plate.
Since heat energy wants to move from the source to another medium that’s cooler, the heat is being transferred from the chips to the lower temperature cold plate.
At the board level, conduction cooling is done by transferring heat from the components through a conduction frame to the card edge and to the “cold wall” of the chassis. To maximize the heat transfer from the components to the cold wall, it is important to minimize the thermal resistance of this path. This is done by using materials with low thermal resistance and wedge locks with higher clamping force.
For many years, conduction cooling has been the mainstay of thermal management for rugged systems. Though it still plays a major role, there are limits as to how much heat conduction cooling alone can dissipate. Most traditional conduction-cooling methods are unable to disperse the heat generated by today’s hotter cards. Where once it was commonplace to have 50W cards, 120W to 200W cards are becoming more common.
Thermal Management in Rugged Computer Systems
This white paper looks at the different cooling techniques available and aims to provide clarity on how to choose the best solution.